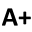Suppose that a 2012 National Health Interview Survey gives the number of adults in the United States which gives the number of adults in the United States (reported in thousands) classified by their age group, and whether or not respondents have ever been tested for HIV. Here are the data:
|
Age Group |
Tested |
Never Tested |
|
18–44 years |
50,080 |
56,405 |
|
45–64 years |
23,768 |
48,537 |
|
65–74 years |
2,694 |
15,162 |
|
75 years and older |
1,247 |
14,663 |
|
Total |
77,789 |
134,767 |
Discuss probability. What is its history? What is the theory of probability? How is it calculated? What are the advantages and disadvantages of using this technique?
1. Identify and discuss the two major categories of probability interpretations, whose adherents possess conflicting views about the fundamental nature of probability.
2. Based on this survey, what is the probability that a randomly selected American adult has never been tested? Show your work. Hint: using the data in the two total rows, this would be calculated as p (NT) /( p (NT) + p (T)), where p is probability.
3. What proportion of 18- to 44-year-old Americans have never been tested for HIV? Hint: using the values in the 18–44 cells, this would be calculated as p (NT) / ( p (NT) + p (T)), where p is probability. Show your work.
Submit your (2-3 pages) paper by the end of this module.
Part 2 SLP:
For the third component of the Session Long Project, write a (2-3 pages) paper in which you:
1. Develop a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis based on the data you have collected.
2. Discuss why you have chosen the hypotheses you developed above. Be sure to discuss the concept of null hypothesis in your response.